Chlamydomonas
Classification
Sub-division - Algae
Class - Chlorophyceae
Order - Volvocales
Family - Chlamydomonadaceae
Genus - Chlamydomonas
[1] STRUCTURE
1. Thallus is unicellular and motile.
2. The cell is usually oval in shape. (Sometimes spherical, oblong, pyriform, or ellipsoidal.)
3. The cell is surrounded by a cell wall. It is narrow at its anterior end and broad at the posterior end.
4. Anterior end bears two closely situated flagella (whiplash type).
5. At the base of each flagellum lies a blepharoplast or basal granule.
6. A small projection or papilla, known as apical papilla, is present in between the two anteriorly inserted flagella.
7. At the base of each flagellum one contractile vacuole is present.
8. Just’ near the cell wall, towards the antero-lateral part of the cell, lies an orange or red coloured spot, called as stigma or eye spot.
9. The broad posterior part has a large, massive and a single cup-shaped chloroplast. The thin sides of the chloroplast cup extend towards the anterior end.
10. The broad portion of the chloroplast has a single pyrenoid (sometimes two to many).
11. The cavity of the cup-shaped chloroplast is completely filled with the cytoplasm in which lies. a single nucleus.
12. Many volutin grains, the main reserve food product, are irregularly distributed in the cytoplasm.
Read This- Life cycle of Volvox
Reproduction
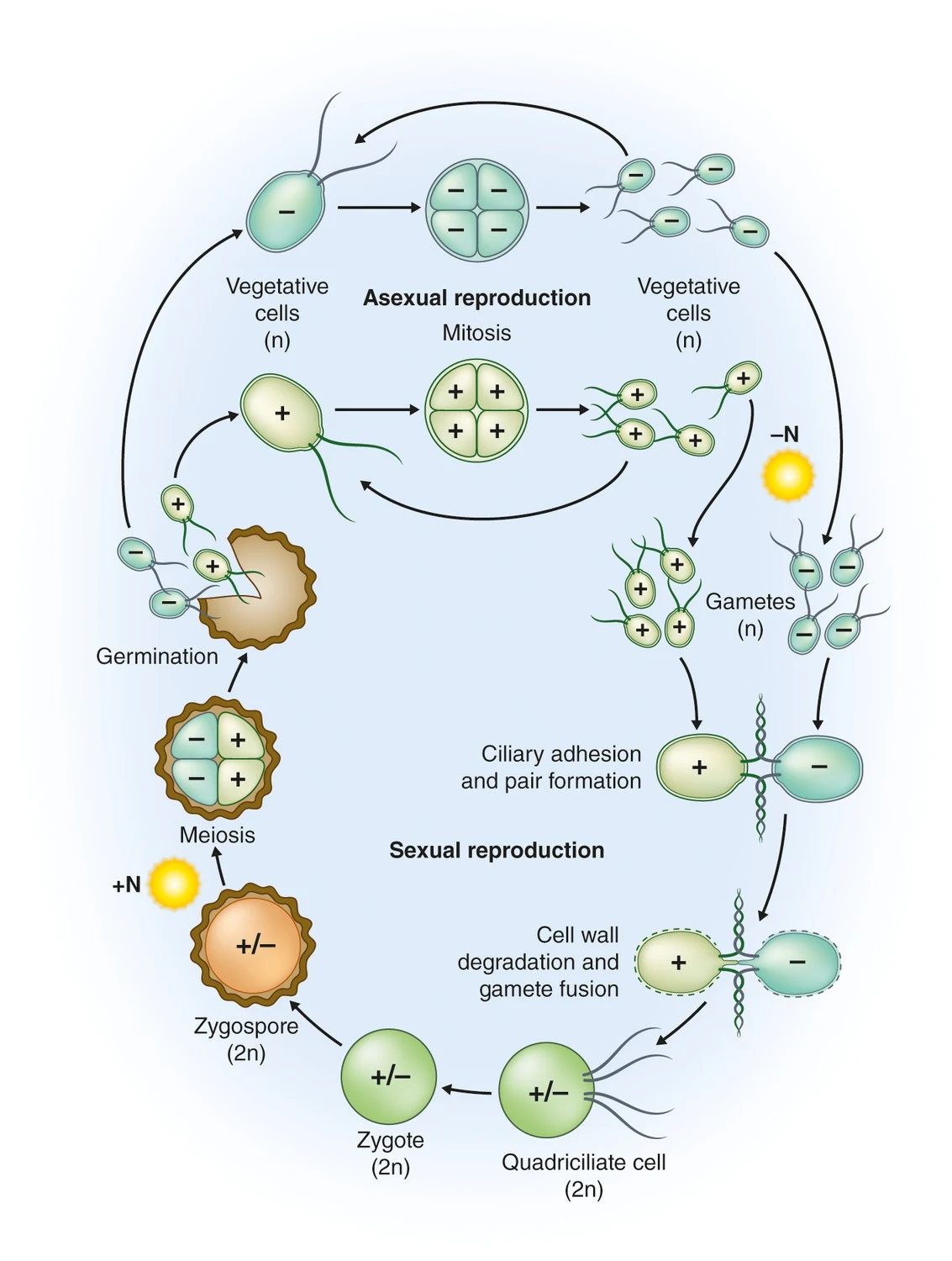
Both asexual and sexual reproductions occur in Chlamydomonas.Asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction takes place by the following methods:
Zoospore formation: Zoospores are formed when the conditions are favourable. During the formation of zoospores the cell becomes quiescent (nonmotile). Its flagella are retracted or discarded. The contractile vacuoles disappear. Its protoplast divides longitudinally into two. It is followed by a simultaneous division of each daughter protoplast and sometimes by a third series of division. Each division of the protoplast is preceded by the division of the nucleus into many parts. Thus each cell produces 2-16 pieces. Each piece secretes a wall around it and forms two flagella. Contractile vacuole and pigment spots also soon appear. In this way 2-16 swarmspores or zoospores are formed within the parent cell. The zoospores or swarmspores are liberated by gelatinization or by the rupturing of the patent cell wall. Each of them develops into a new Chlamyclomonas plant. This process of division is repeated every 24 hours. Thus by the end of week, from one parent plant about 2,000,000 individuals are formed.
Aplanospore formation: Aplanospores are formed under conditions of drought. The zoospores instead of being liberated found up and develop into aplanospores. Aplanospores germinate directly or divide to produce zoospores on the approach of favourable conditions.
Read More-
👉Life cycle of volvox, Sexual Reproduction in Volvox,
👉Protista Kingdom प्रोटिस्टा जगत
Palmella stage
(It is known as Palmella stage because of its resemblance with another alga—Palmella of the order Tetrasporales).
This stage is formed under less favourable, but not very dry conditions. In this condition, the ponds are gradually drying up. So the plants are growing on damp soil. The daughter cells are produced by the division of the parent cells. These cells do not develop flagella. They are embedded in the mucilage formed by the gelatinization of the parent cell wall. The daughtei’cells divide further into four. Their cell walls also become mucilaginous. Thus a large number of small non-motile structures are formed. They are embedded in jelly-like substance. In this way, an amorphous colony is formed. It has hundreds or thousands of cells. All its cells are embedded in a common gelatinous matrix. This stage is known as the palmella stage. It ;s named so because the older phycologists thought it to be a species of an alga named Palmella. This is however, a temporary phase. Soon all small daughter cells develop flagella and become motile.Sometimes, cells of the Palmella stage develop into thick-walled hypnospores. These are red coloured due to the presence of a red pigment called the haematochrome.
Sexual reproduction
The sexual reproduction may be isogamy to anisogamy and oogamy. At the time of sexual reproduction, the protoplast of a cell divides into 16,32 or even 64 biflagellate gametes. The gametes may be naked called gymnogametes. Or they may be enclosed in a cell wall called calyptogametes. The walls of calyptogametes may be left behind as the gametes fuse in pair or they may be retained.
Isogamy: In this case, the fusing pairs of gametes are naked and equal in size. It occurs in Creinhardi and C.Iongistigma.
Anisogamy: In this case, fusing pairs are similar in shape but different in size. The female cell produces four larger macrogametes. The male cell produces eight smaller microgametes. It occurs in C.monocia, C. Braunii etc.
Oogamy: In this case, the fusing gametes are different both in size and shape Oogamy occurs in Ccorcifera and C.oogonium. rhe frmale call functions as oogonium. It produces a large macrogamete or egg. The male cell functions as antherozoid. It produces 8, 16 or 32 small spherical biflagellate microgametes or sperms. The egg is not completely non-motile. It is surrounded by a number of motile male gametes or sperms.FertilizationThe flagella disappear during fertilization. In some species, flagella may persist. Therefore, quadriflagellate zygote may remain motile for more than fifteen days. Then it secretes a wall. Sexual process is chemically regulated. Fusion occurs between the gametes of different cell types.
Germination of zygospore.
1. The resting zygospore or zygote secretes thick wall. It becomes red as the chlorophyll is masked by haematoohrome. Its starch is converted into fats.
2. Before germination the protoplast of the zygote becomes green. Its nucleus divides twice followed by the division of the protoplast into four parts.
3. Each uninucleate piece of protoplast is metamorphosed into a biflagellate zoospore. Thus four zoospores are formed.
4. They are liberated in water by the rupturing of the zygote wall. Meiosis takes place during the formation of zoospores from the zygote. They zygote is diploid. But the normal vegetative cells are haploid.
यह भी पढ़ें 👇
👉मूत्र रंग सामान्य एवं असामान्य लक्षण (Symptoms)
👉जीभ के रंग के आधार पर रोगों का परीक्षण
👉योनि (Vagina), The Vagina, Anatomy of the vagina, Sexual stimulation male and female
👉Human Digestive System, मानव पाचन तंत्र, एवं पाचन तंत्र के विकार
👉मानव नेत्र, Human Eye, नेत्र की संरचना एवं नेत्र के प्रमुख भाग
👉What is Skin? Structure and Function of Skin.
👉रुधिर किसे कहते हैं, रक्त किन - किन पदार्थों से मिलकर बना होता है
👉जीवों में प्रजनन संबंधी महत्वपूर्ण बिन्दु
👉NERVOUS SYSTEM, FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD, SENSE ORGANS EYE AND EAR
👉The Brain, Human brain, Parts of Brain
👉FULL NAME OF SAARC, NAME OF SAARC COUNTRIES, MEANS OF SAARC
👉International Airports of India
👉लोकसभा क्या है, What is lok sabha
👉सिंधु घाटी सभ्यता अथवा हड़प्पा सभ्यता किसे कहते हैं ? What is Indus Civilization Period?
👉इतिहास, पाषाण काल, HISTORY FREE PDF NOTES
👉Life cycle of Ectocarpus and Practical work study of Ectocarpus
👉Life Cycle of Vaucheria, Practical work and Lab Study of Vaucheria
👉Life cycle of Chara, Practical Work and study of Chara, Structure of Chara
👉ऊष्मा किसे कहते हैं? ऊष्मा के संचरण की कितनी विधियाँ हैं ?
👉विलयन किसे कहते हैं? What is solution?
👉सरल आवर्त्त गति किसे कहते हैं सरल लोलक किसे कहते हैं
👉What is Explosive, विस्फोटक पदार्थ के नाम
👉प्रत्यास्थता (Elasticity), किसे कहते हैं, एवं हुक का नियम (The Hooke's Law)
Identification
Sub-division—Algae. (1) Presence of a simple thallus, (2) Chlorophyll present, (3) Cell wall made of cellulose.
Class—Chlorophyceae. (1) Presence of a definite nucleus, (2) Chloroplast present, grass green colour, (3) Presence of starch, (4) Reproductive structure motile and flagella equal in length.
Order—Volvocales. (1) Thallus motile, (2) Protoplast with contractile vacuoles.
Family—Chlamydomonadaceae.
Genus—Chlamydomonas, (1) Oval or pyriform shape of the thallus which is unicellular, (2) Cup-shaped chloroplast, (3) Presence of an eye spot, (4) Formation of Palmella stage.
Hints for collection
It is found free-swimming in freshwater, stagnant pools and ditches. It also occurs on damp soil and mostly forms a green surface layer on the water.
👉Life cycle of volvox, Sexual Reproduction in Volvox,
👉Protista Kingdom प्रोटिस्टा जगत